MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS
1 . The mechanical properties are those which are associated with the ability of the material to resists mechanical forces and loads .
2 . These mechanical properties are metal include strength , stiffness , elasticity , plasticity , ductility , brittleness , malleability , toughness , resilience , creep , hardness .
There are some properties of metals which given below :-
1 . STRENGTH :-
It is the ability of the material to resits the external applied force without breaking or yielding . The internal resistance offered by a part to an externally applied force called stress .
2 . STIFFNESS :-
It is the ability of the material to resists deformation under stress . The modulus of elasticity is the measure of stiffness .
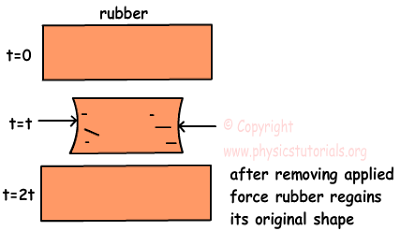
3. ELASTICITY :-
It is the properties of material to regain its original shape after deformation . when the external force is removed.
4 . PLASTICITY :-
It is the properties of material which retain the deformation produced under load permanently .
5 . DUCTILITY :-
A dctility material must be both strong and plastic . The ductility is usually measured by the terms percentage elongation and percentage reduction in area . The ductile material commonly used in engineering practice . like steel etc .
6 . BRITTLENESS :-
It is the properties of a material opposite to ductility . It is the properties of breaking of a material with little permanent distortion . Brittle material when subjected to tensile load , Cast iron is a brittle material .
7 . MALLEABILITY :-
It is a special case of ductility which permits material to be rolled or hammered into thin sheets . A malleable material should be plastic but it is not essential to be so strong .
8 . TOUGHNESS :-
It is the material to resists fracture due to high impacts load like hammer blows . The toughness of the material is decrease when it is heated . It is measure in amount in which that a unit volume of the material has absorbed after being stressed upto the point of fracture .
:9 . MACHINABILITY-
It is the properties of a material which refers to a relative case with which a material can be cut . The machinability of a material can be measure in a number of way such as comparing or thrust require to remove the material at some given rate .
10 . RESILIENCE :-
It is the properties of a material to absorb energy and to resists shock and impact loads . It is measured by the amount of energy absorbed per unit volume with in elastic limits .
11 . CREEP :-
When a part is subjected to a constant stress at high temperature for a long time , it will undergo slow and permanent deformation . called creep .
12 . FATIGUE :-
When a material is subjected to repeated stresses , it fails at stress below the yielding point stress . it is called fatigue . The fatigue is caused by means of a progress crank formation which are usually fine and of microscope size .
13 . HARDNESS :-
It means the ability of a metal to cut another metal . The hardness is usually expressed in numbers which are dependent on the method of making the test .













No comments:
Post a Comment